Opportunities and Risk for Traditional Banks in Embracing Open Banking

Technology has simplified our lives by making the processes easier and integrating into our daily routines. Today we cannot imagine making payments without using UPI, that’s the impact technology had on the payment systems. UPI has achieved such rapid success in a short period. The total number of payments done through UPI channel for 23-24 stands at 13.11 trillion which is around 80% of the total digital payments made in India during the period. Beyond its user-friendly interface, it’s the interoperability of UPI that stands out as a game changer. A major credit for the growth of instruments like UPI goes to the Open Banking. It has helped in connecting traditional banks and innovative FinTechs through APIs to provide solutions for payments, lending, investing etc. Open banking has fostered an era of collaboration between the banks and FinTechs. It has been a win-win for all i.e. Banks, FinTechs, and customers.
What is Open Banking?
Open Banking refers to access to the customer data of the banks to third-party developers and service providers via APIs to develop and offer competitive products and services. The sharing of data to the third party API is solely based on the discretion/consent of the customer. The concept originated around 2007 with the European Union’s implementation of the “Payment Services Directive” (PSD), creating uniform payment solutions across EU nations. After that in 2015, “Payment Services Directive 2” (PSD 2) was introduced, to widen the scope of payment systems. In India, open banking began with RBI establishing an entity called “Account Aggregator (AA)” in 2016.
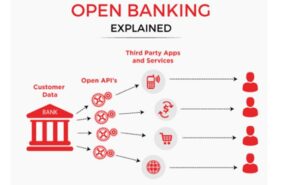
Traditional Banks and Open Banking:
The basic premise of open banking revolves around the ownership of customer data, with customers rightfully owning their financial information instead of it being possessed by banks, which simply collect and store the data. This shift has given customers the freedom to choose applications through which they want to conduct their financial transactions. Initially, open banking caused unease for traditional banks as they had to share customer data with competitors, who were using it to sell their products/services and it is evident that third-party apps utilizing open banking APIs are gaining ground over traditional banks due to their more streamlined, structure and focused approach.
In India, as of April 2024, third-party apps such as Phonepe (48.87%), Google Pay (37.5%), and Paytm (8.30%) hold a significant market share for UPI payments.These apps collectively hold nearly 95% of the total market share for UPI Payments.
Nevertheless, many banks have adapted to this shift and begun innovating their products and services either independently or in collaboration with other FinTechs to enhance customer experience and expand offerings. Open banking has spurred significant developments in lending, investment, and payment spaces.
Opportunities for Traditional Banks in Embracing Open Banking
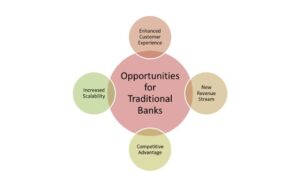
- Enhanced Customer Experience
Open banking allows fintech companies to provide unique and customer friendly products and services to the customers, highly improving the customer experience. To enhance customer experience, banks worldwide are now collaborating with Fintechs to offer personalized and unique products, services, and propositions. The data that banks possess serves as valuable input for Fintechs equipped with AI and ML capabilities to provide deep insights into customer needs. An instance of this partnership is the integration of chatbots into banking services. Today in India, all major banks have chatbot facilities for their customers. For instance, SIA, the chatbot of State Bank of India developed by Payjo, a Silicon Valley and Bengaluru-based fintech company can handle more than 10,000 queries per second. Chatbots have proven to be useful in providing instant solutions to customer queries with 24 x 7 availability. Online lending market place created by SIDBI in collaboration with OPL a Fintech i.e. www.psbloanin59minutes.com has served more than 7 lac plus MSME customers disbursing more than Rs 74000 crs by partnering with 20 plus banks. The portal serves as on open marketplace allowing customers to chose a bank if its choice to avail loan specifically for MSME segment.
- New Revenue Stream
Open banking can be used to create new revenue streams for banks by generating profits and offsetting potential losses due to data sharing. One method for generating revenue is to form partnerships with FinTechs to offer innovative products or services. Banks may open up as a market place allowing fintech to pitch for their products directly to the customers. For example, Niyo Global—a fintech specializing in international payments—has collaborated with many banks such as DCB Bank and Equitas Small Finance Banks.
Banking as a Service, where banks offer their infrastructure, allowing FinTechs using open APIs to connect with the bank’s database and provide banking-related services to their customers is also a way to generate revenue for banks.
Banks using the account aggregator services and combining it with their database can create individual customer profile and create personalized products and services, which can help in increasing the customer engagement and sales of the product.
- Competitive Advantage and Increased Innovation.
By fostering partnerships with highly innovative FinTechs, banks can upgrade their existing offerings both in terms of products and services while creating a competitive advantage. Banks by carefully analyzing and understanding the needs of their individual customers should on-boarding a fintech who has expertise in providing the products or services. The key to gain competitive advantage is to become the first mover or be the first to offer the product or service.
To remain competitive banks today, need to act as a financial marketplace providing all the financial products and services on a single platform, like payment solutions, investment solutions, insurance solutions, tax planning etc.
Open banking has also incentivized banks’ increased innovation efforts in providing technologically advanced products counteracting challenges posed by FinTech companies.
With changing time and technological boom customer preferences have changed, leading to demand for services in digital form as compared to brick and mortar. Customers now prefer banks and financial service provider who are able to provide them technologically advanced solutions for their financial management.
- Increased Scalability
Open banking solutions are scalable since they are mostly provided through applications or technological platforms which can reach large numbers of people effectively. Fast-paced internet technologies such as smartphones have further supported large-scale implementation.
The integration of open API applications has had a significant impact on boosting financial inclusion in India, allowing for account openings through Video KYC (Know Your Customer) processes in addition to eKYC method. Another example of scalability is UPI, the total number transactions for the FY 2023-24 done through UPI stands at 13.1 trillion.
Risks Associated with Embracing Open Banking
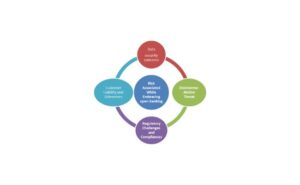 Fig 3: Risks Associated with Open Banking
Fig 3: Risks Associated with Open BankingData Security Concerns
Open banking allows access to sensitive customer data. However, this data is at risk if the systems of the data-accessing FinTechs are weak or not up to date, resulting in third-party risks. This may also lead to the risk of a data security breach, resulting in the leakage of sensitive customer data. Data leakage has serious consequences and may lead to cyber fraud and privacy issues. Hence, it becomes extremely important to establish security and encryption guidelines before giving third-party applications access to open APIs.
For open banking to succeed, customers must be assured that they retain authority over their financial information and strong security measures are in place to safeguard their data and ensure that it is only accessed and utilized with proper authorization both at the level of bank and third party provider.
- Disintermediation Threat
One of the biggest threats that banks face with open banking is disintermediation. With customers being owners of their own data, there is a high chance that customers might opt for any third-party application for their financial needs such as payments, lending, and investment solutions. Hence disintermediation or bypassing, results in loss of business for banks which are then rendered as only basic financial service providers. It is crucial for financial service providers and banks to take the competition head-on by providing innovative products and services to compete with FinTechs and other financial institutions and also to remain relevant in the long run.
- Regulatory Challenges and Compliances
Open banking has just started to gain ground around the world, major challenges that financial institution and third party providers have is to ensure compliance and interoperability in cases where they are working in different geographies with different regulatory guidelines.
Regulators encounter challenges in managing the evolving technology landscape while ensuring that both financial institutions and third-party providers take effective measures to prevent potential breaches or thefts, when sharing customer data.
It is for the regulators to instill confidence among customers regarding safety and security of their data and also promote a whole hearted adoption of open banking by traditional banks. Regulators have to tread a very fine line in order to ensure compliance and also support innovation.
- Customer Liability and Grievances Redressal: With multiple parties involved in open banking model, grievances related to customer liability arising out of fraudulent transactions or misuse of data are also needed to be addressed, so that defaulting party can be identified along with necessary recourse for the customer losses arising out of these incidents. This is of prime importance for the success of open banking and wide spread acceptability of open banking.
The way forward
Moving forward, we should expect increased collaboration between fintech companies, banks, and regulators to create more personalized solutions for customers to satisfy their financial needs. For traditional banks to sustain and grow their market share, they must take a lead in adopting to open banking and rethink their business models to be able to respond to dynamically changing technologies. However, to ensure widespread adoption by customers, it is crucial to develop robust data protection measures, standardized APIs, and clear consent mechanisms to safeguard customer data. Furthermore, educating consumers about the benefits of open banking and promoting transparency will be crucial in building trust.
Conclusion
Technology has consistently made life easier for people, especially in the financial sector, by enhancing access to financial services. In the last decade, we have seen some of the disruptive innovations by fintech companies, which have changed our lives for the better. Open banking is one such platform that allows the use of technology to provide a wide range of solutions to customers, opening up the entire spectrum of financial services and offerings. Open banking has led to the adoption of more innovative products and services by banks in order to keep up with fintech companies, through partnerships or in-house development. Open banking has the potential to disrupt the technology in the financial world. We have seen solutions that have reached the last mile to provide financial inclusion and services which couldn’t have been thought earlier.
Open banking is a win-win situation for banks, customers, and FinTech companies, it is likely to be the theme for next decade and a space to watch out.




