USERS’ DUTY IN CYBER SECURITY
Introduction
Technological advancement has brought many conveniences to the modern society. “Any where any time” work culture is the paradigm shift of attitude is the biggest benefit for the individual and corporate world. Work at home is the outcome of such technological advancement in cyber world. We are able to settle electric and water bills, insurance premium etc sitting in home without attending a long queue. Transacting in bank account, sitting at a remote place, is a matter of delight for the customer and extremely convenient for the banker. This is the basis for a move to cashless culture. But the security of everything is a threat for digital transformation. The customer’s personal and account details are extremely important for both bank and its customers. Those information needs to be kept confidential from others. It is only between the customer and authorized bank staff to know such information. Any leakage of information is called security breach. This may cause huge financial loss and reputation damage to bank and much collateral impairment to both.
Background
On 19 October 2016, the country woke up by the news of State Bank of India. The Bank blocked 6 lakh debit cards after a reported malware-related breach in a non-SBI ATM network. This was India’s largest financial data breach. Nearly 32 lakh debit cards across 19 banks of the country were compromised. As per the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), 90 ATMs were impacted and at least 641 customers lost Rs 1.3 crore in fraudulent transaction. Banks have advised their customers to change PINs and confine themselves to own bank ATMs. Meanwhile, all the customers are worried about the security of their bank accounts and debit /credit cards. It is worth noting that total transactions are expose nearly 2.59 crore credit cards issued by 56 banks had a volume worth Rs 24,341 crore via points of sale (POS) and Rs 202 crore through ATMs. Banks are definitely revisiting their network security to prevent any compromise. RBI is also trying to stay one step ahead by introducing several security features, including chip-based cards and two-factor authentication etc. All the above, the customers need to take the initiative to prevent being conned. We can take various precautionary steps to steer such mishaps.
Areas where we are usually duped by fraudsters
A. Automated Teller Machines (ATMs)
ATM fraud involves theft of identity or information of the customer on the card. This stolen information is used by the fraudster to make ATM withdrawals or online and offline transactions. The ATM machines have become a favored target of fraudsters
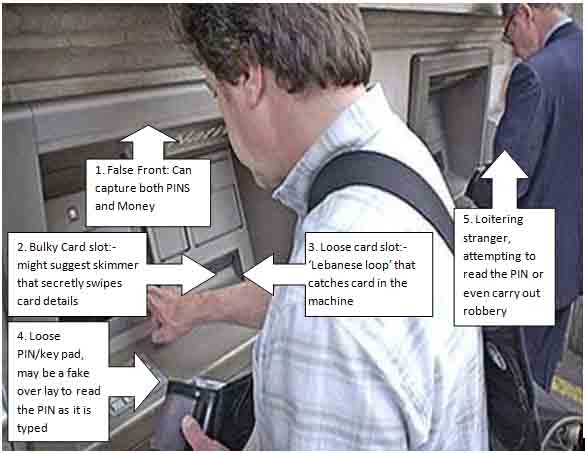
- False front
It is little difficult to detect as the fake front completely covers the original machine. Normally, it is installed on top of the machine. This allows fraudsters to take our PIN as well as money. Sometimes, tiny, pinhole cameras may be placed on the machine or even the roof at strategic positions to capture card PIN and card CVV.
- Bulky slot
Card skimmer are devices , installed on the card reader slot to either copy the information from the magnetic strip of the card or steal the card itself. If the slot feels slightly bulky or misaligned, the probability is that an additional card reader slot has been placed on top of the actual one. This passes on the card information to third party very easily.
- Loose slot
This is also card skimmer. If the slot is loose, it indicates the presence of a duplicate slot. This is known as ‘Lebanese loop’. This is a small plastic device with a barb that holds the card back in the machine. We may think the machine has swallowed the card or it has been stuck. But during the process the card information is being divulged.
- Fake keypad
This is placed on top of the actual keypad. Such keypad feels little spongy and loose. On this type of key board, PIN should not be entered.
- Shoulder surfers
These are people lurking in the ATM room or outside. They always try to assist people and through this they read and remember the PIN. Sometimes they peer over the shoulder to read the PIN.
B. Online transactions
The convenience of e-shopping, online bill payment and digital transactions sometimes creates the path for the fraudsters to steal information and identity of the users. This may be through computer or smart phone. This can then be used for unauthorized transactions. There are various ways this card information could have been stolen.
- Pharming: – Fraudsters reroute us to a fake website that looks similar to the original. Immediately when we conduct transactions and make payment by the card, the detail information is e stolen.
- Keystroke logging: – Here, the user unintentionally tempted to download a software, which perpetrate the fraudster to trace your key strokes and steal the password, card and Net banking information.
- Use of Public Wi-Fi: – When we use to carrying out transactions on our Smartphone in public Wi-Fi, it creates a good hacking opportunity for thieves to steal our card details.
- Malware: – This is malicious software that can damage computer systems at ATMs or bank servers and allows fraudsters to access confidential information. Malware can be delivered in several different forms, depending on the intention of the person who developed it. Most important of them are
- Trojan horses:-When it is activated, damages the host computer and attempts to steal files or passwords.
- Spyware: – It infects and operates on a user’s computer to monitor user activities and extract information by tracking keystrokes to determine login and password information.
- Ransomware:-It locks a user’s computer and then demands a ransom payment to restore access.
As malware and viruses most commonly infect PCs, it is to be ensured that machines have active antivirus software, firewall, a strong password and a BIOS password. Beyond that we should also avoid downloading apps or programs from suspicious websites.
C. Merchant or point-of-sale (POS) theft
This is the simplest method of stealing information. Customer’s card is taken by the salesperson for swiping and the information from the magnetic strip is copied. This resource is utilized later for illegal transactions.
D. Phishing & vishing
Phishing involves theft of identity through spam mails which seem to be from a genuine source. Vishing is essentially the same through a mobile phone using messages. Unknown user is tricked into revealing password, PIN or account number.
E. Cards using other’s documents
Here the fraudster prepares new cards by using personal information that is stolen from application forms or other lost or discarded documents.
PREVENTIVE ACTIONS BY USERS TO AVOID CREDIT OR DEBIT CARD FRAUD
A. ATM safeguards
Do not use the ATM which appears dirty and unrepaired. It may be a fake machine set to capture the card information
Following things should be kept in mind before using ATM
- Do not use ATMs with unusual signage, such as a command to enter your PIN twice to complete the transaction.
- Check the machines that appear to have been somewhere altered, crooked, loose or damaged. It may be an indication that someone has attached a skimming device at the front.
- Cover the keypad by other hand while entering the PIN to escape any camera attached inside ATM room or at the top of ATM monitor.
- It is advisable to use parent bank ATMs, particularly those attached to a bank branch
- ATM with security guards is always preferred as any tampering of the ATM can be avoided.
- Avoid taking the help of any person loitering outside the ATM or volunteering to assist.
B. Precautions for online operation
- Confirm the legitimacy of the site before use. Well-known and established sites are always preferred for e-shopping. Shopping should be done only on those that are Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)-certified. Those can be identified through the lock symbol next to the browser’s URL box. Prefer the website that uses the ‘https’ protocol instead of ‘http’, where‘s’ stands for ‘secure’. Do not click on options that prompt to save the card details on any site. To protect the privacy of online transactions, use secure code for payment verification.
- Normally, banks deploy ATM network security measures and update the antivirus software on regular basis. We can safeguard transactions by installing anti-virus software in our computer and Smartphone to keep out malware.
- We can also install identity theft detection apps on our smart phone from an official apps store. We can also install software on our Smartphone that enables us to wipe out entire data remotely in case the mobile is lost.
- Use of debit card for E-shopping is much more dangerous than credit card. If the debit card is compromised, the entire cash in the bank account can be wiped away instantly. But in credit card as provision of grace period is there for payment, on complain, the investigation can nail the fraud.
- CVV is very important while shopping on foreign websites where the CVV is the only point of verification. It is advised to use a virtual keyboard to avoid keystroke logging. When we enter the CVV on the site, it should be masked by asterisks.
- We must avoid using unsecured or public Wi-Fi as these are easy targets for identity theft.
- Bank always put transaction alert for any online transaction or ATM withdrawal the moment it takes place. Remember to update the mobile contact number in case of any change.
- Log out properly from social media sites and other online accounts to ensure data security.
- Avoid storing confidential passwords on mobile phones as these can be used by fraudsters.
- Keep changing your passwords from time to time to reduce the probability of theft.
- Use this virtual prepaid card if you are not a frequent shopper, as it expires after a day or 48 hours.
C. Common and offline preventive measures
Some additional precautions we can take to ensure our card’s safety
- Never reveal your PIN, CVV or password to anyone. Make sure not to respond to e-mail/ SMS that ask for crucial personal or card-related information. No bank is authorized to seek card related information from customers on mail or through phone.
- Regularly check bank or credit card statements so that you can detect any unauthorized transaction through identity theft and alert the bank immediately.
- At shops or petrol pumps, where POS machines are used, make sure that the card is not taken by the salesperson to a remote location where you cannot see it as the card information can be easily copied and stolen.
- Ensure that you never sign a blank receipt, and mark through any blank lines or spaces before signing so that nobody can add an additional amount.
D. Password Management
Passwords have become ubiquitous in this digital world. Starting from social media profiles to bank accounts and e-commerce sites everywhere requires a password. Managing and keeping those passwords secure from hackers is essential.
Create a strong password
- Mixing certain characters (@, #, $, &, etc.) in place of letters or numbers create a strong password.
- Minimum of eight characters in password with a combination of lowercase, uppercase letters, numbers and special characters is good
- Unusual combinations are the best. For instance, pick a favorite lyric and use the beginning letters from each word. Try choosing a combination with a pneumonic device for remembrance.
- Random letters on a keyboard can be selected for better protection. Because this will be very difficult to remember.
- Use different passwords for different devices, applications, online accounts and systems
- Never use personal information in password that can be easily guessed (such as birthdays or pets’ names)
- Change password regularly. Never repeat the same set of words.
- Replace the weak or duplicate passwords with stronger, unique passwords
- Keep the password secure
- Never write passwords on slips of paper or in a notepad. Those can easily be lost in a public place and can be stolen.
- With so many passwords and login combinations, it is difficult to remember. Follow some system on designing and sequencing the passwords. Following procedure can be followed
- Password can be saved in a text file, which then can be stored on a password-protected, encrypted USB drive.
- Several password management programs have come to market in recent years. Many of which offer high-quality password management features. Passwords can also be updated from the software, which can generate and save secure passwords on our behalf.
Action point after being cheated
In case of card identity theft or a fraudulent offline or online transaction,
- Report the loss immediately to card provider bank and get the card blocked.
- Make sure that you have the customer care number of the card provider bank.
- After card blocking telephonically follow it up with a letter or e-mail.
- It is also advisable to lodge an FIR at the earliest at nearest police station
- If the bank does not respond within a week, approach the nodal officer of the concern bank.
- If there is no positive response from the bank within 30 days, contact the banking ombudsman appointed by the RBI
- If there is further any problem, approach the court of law for redressal.
Conclusion
The customer must remain alert while scrutinizing statements and getting SMS alert, managing password, while using debit-credit card for online and ATM transactions. It is the responsibility of the user. A customer is not liable for a third-party breach, or where negligence or fraud is on the part of the bank, if the customer informs the bank of the fraud within 3 working days of receiving a communication from the bank on any unauthorized transaction. A Stitch in Time Saves Nine.
References:
- Credit, debit card frauds and how you can avoid them, By Riju Dave, ET Bureau|
- Everything we know about the great Indian debit card hacking, Madhura Karnik, OBSESSION,Future of Finance,October 24, 2016 Quartz India
Author
ALEKH KUMAR SAHOO
CHIEF MANAGER(FACULTY)
STAFF TRAINING CENTRE,BHUBANESWAR, Union Bank of India
Published : Banking Finance, December, 2018




